Scheduling of Manufaturing Systems
Summary
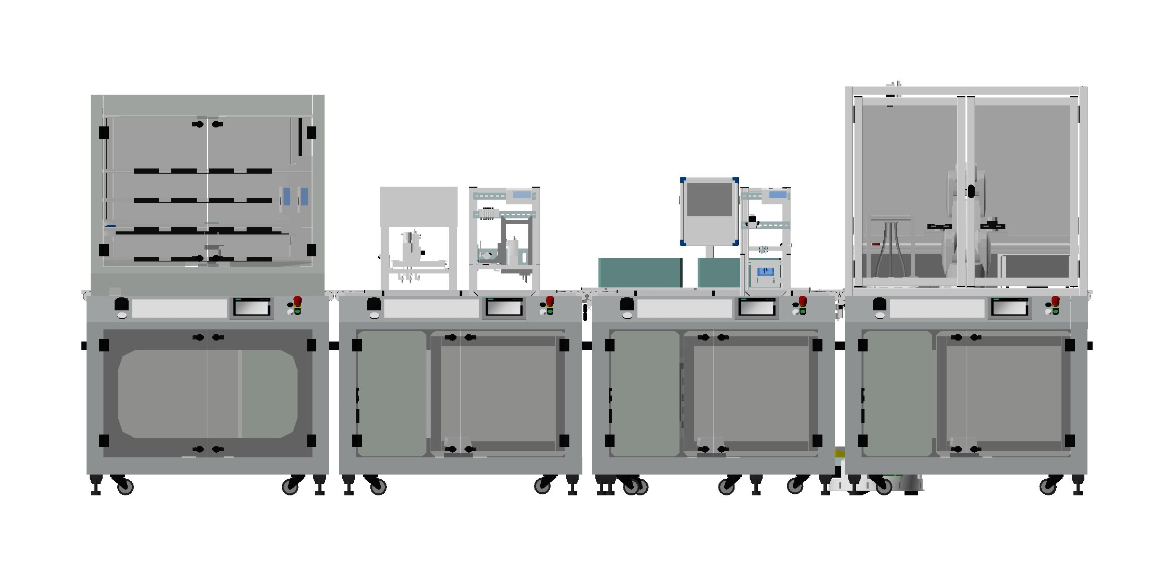 |
Existing production planning solutions are neither easy to use nor performance adaptive and optimal. In this project we are addressing this challenge from two different angles, that is, to develop a novel drag-and-play production task modeling and controller design framework, and to develop a novel fault-tolerant AGV fleet management framework and tool. Our solutions can enhance AGV fleet management, including the level of automation and fault tolerance, and improve controller design efficiency and responsiveness. Together, they can improve the overall productivity and cost reduction.
Contributions
For the production scheduling part, we use discrete event systems (DES) for modelling a general class of reconfigurable manufacturing systems in the low level and employ supervisor synthesis tools for the automatic synthesis of (sub)-optimal plans and schedules
This work attempts to overcome the drawbacks of existing modelling techniques for low volume high mix productions (LVHM) manufacturing systems, which often lack built-in guarantee for requirement compliance or behaviour correctness and lack tools that can automatically adapt to new system functionalities and user requirements after system reconfiguration, while still supporting a range of different optimization techniques to be employed for solving the scheduling problem.
Drag-and-play production task modeling and controller design framework
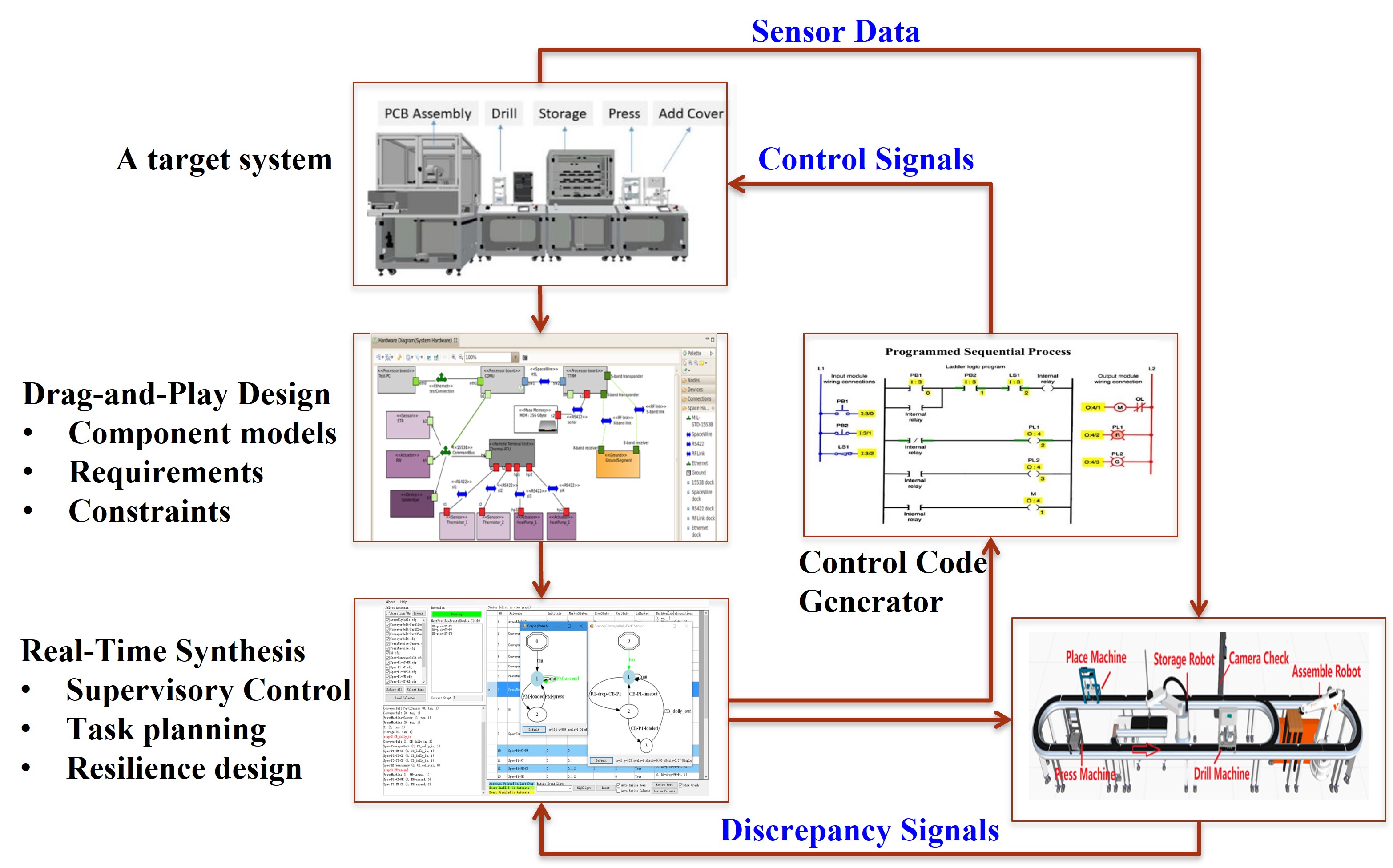
Manufacturing planning and control typically contains the following steps: system design, real-time planning, supervisory control execution, feedback and replanning. How to automate the system design and planning is one challenge for the industry. Existing approaches typically start from scratch manually, even though many components in a target system are functionally similar to existing ones, resulting in huge waste of knowledge accumulated in the past. To maximize knowledge reusability and shorten the design process, a novel production scheduling and controller design framwork is proposed.
 |
|
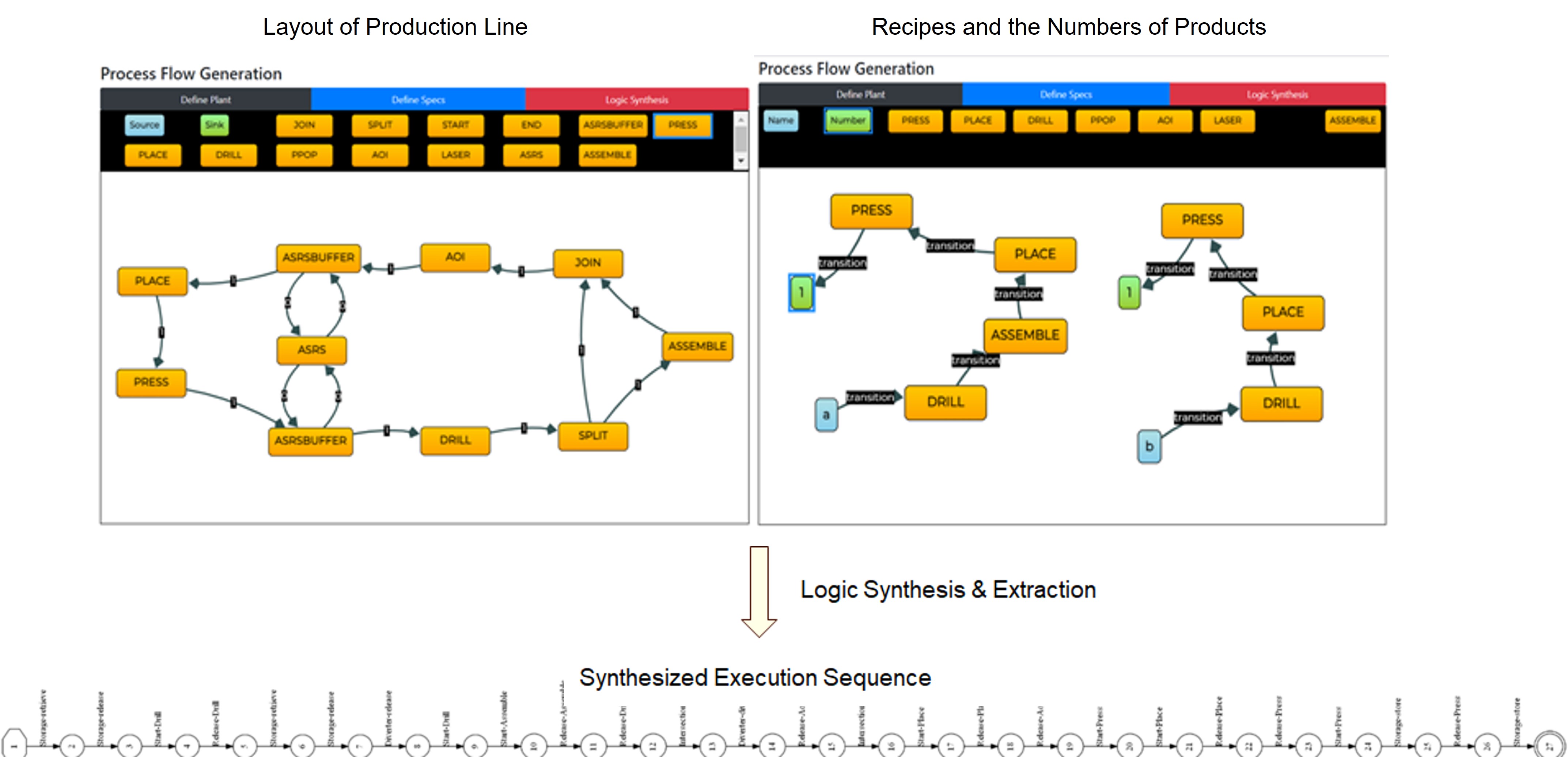
Discrete-event system based drag-and-play tool
 |
The tool supports different optimization algorithms to be deployed in the backend, including: |
Integrated Drag & Play System
For a typical design procedure in the Drag & Play system, a user drags existing component templates from the extendable database and builds the layout of a production line. After that, the user specifies production recipes. With the layout and recipes, the tool automatically generates formal component and requirement models as finite-state weighted automata. Then, the tool calls an external synthesis tool SuSyNA to generate a supervisor to ensure logic correctness and performance optimality. The output operational sequence can be directly executed by the system via its MES.
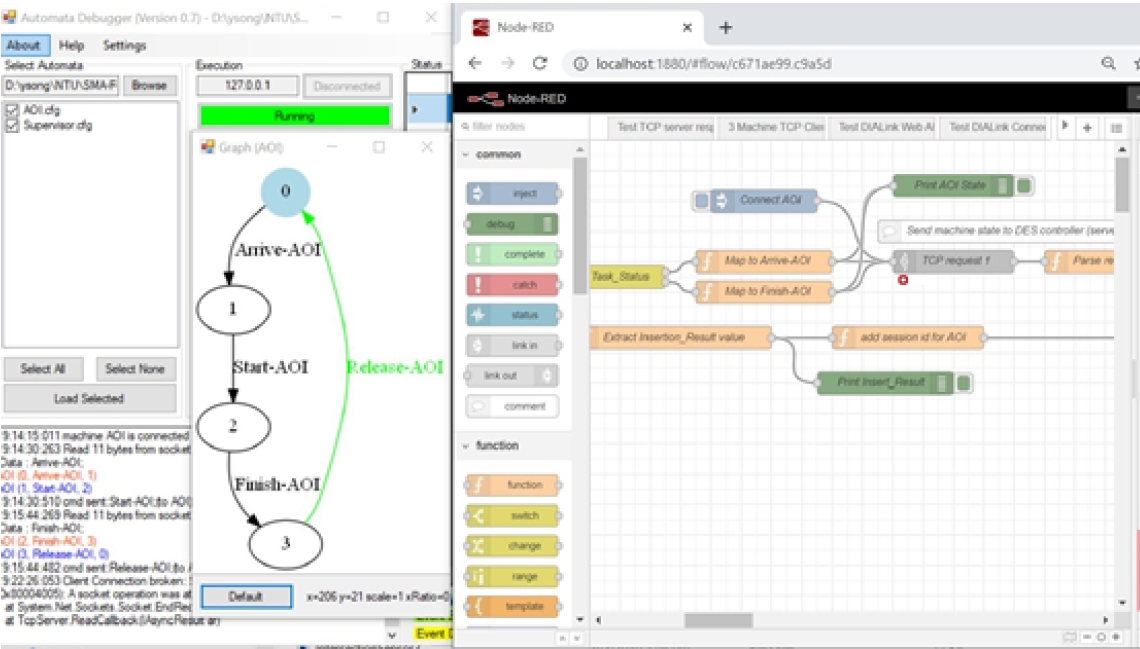 |
Features involved in our system: |
References
Ware, Simon and Su, Rong, “Time Optimal Synthesis Based Upon Sequential Abstraction and Its Application to Cluster Tools.” IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering. Volume: 14, Issue: 2, pages: 772-784, April 2017.
Ware, Simon and Su, Rong, “Progressive time optimal control of reactive systems.” Decision and Control (CDC), 2015 IEEE 54th Annual Conference: 3542-3547.
Ware, Simon and Su, Rong, “Synthesis time optimal accepting traces using language projection and pruning.” Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2015 IEEE International Conference: 1363-1368.
F. J. Yang, N. Q Wu, L. P. Bai, Y. Qiao, M. C Zhou, R. Su, (2018). "Petri Net-Based Efficient Determination of Optimal Schedule for Transport-dominant Single-Arm Multi-Cluster Tools," IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 355-365.
F. J. Yang, K. Z Gao, I. W. Simon, Y. T. Zhu, R. Su, (2018). "Decomposition Methods for Manufacturing System Scheduling: A Survey," IEEE/CAA, vol. 5, no. 2.
F. J. Yang, N. Q. Wu, K. Z. Gao,Y. T. Zhu, R. Su, Y. Qiao, I. W. Simon, (2018). "Efficient Approach to Cyclic Scheduling of Single-arm Cluster Tools with Chamber Cleaning Operations and Wafer Residency Time Constraint," IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 196-205.
F. J. Yang, N. Q. Wu, Y. Qiao, R. Su, (2018). "Polynomial Approach to Optimal One-wafer Cyclic Scheduling of Treelike Hybrid Multi-Cluster Tools via Petri Nets," IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 270-280. [2021 Hsue-shen Tsien Paper Award].